|
Offsetting CO2 Emissions from Ocean Transport of Completed Cars for Europe Tokyo - June 15, 2022
Completed cars from Mazda Motor Corporation (Representative Director, President and CEO: Akira Marumoto; Headquarters: Aki-gun, Hiroshima Prefecture) were loaded on the MOL-operated Beluga Ace, and the vessel departed the Port of Hiroshima on April 18, arrived at the Port of Bristol, the U.K., on May 28. CO2 emissions during the voyage between Japan and Europe reached about 4,000 tons including all processes from production through consumption of fuel oil. The calculation method of the volume was properly verified by the third-party verification body Bureau Veritas. The entire process, from calculating CO2 emissions including the verification process to compensating all CO2 emissions with carbon credits, was also certified by the third-party certification body Climate Neutral Commodity (Note 2). 
Loading cars on the Beluga Ace at the Port of Hiroshima, and loaded Mazda cars in the hold of the vessel. Image by MOL. MOL used carbon credits generated from afforestation and reforestation projects in Ghana and China (Note 3) for this initiative. Both projects are certified by the international carbon credit standard management body Verra (Note 4), and the credits were generated within the past five years. In addition, these projects contribute not only to absorbing and removing CO2 from the atmosphere (Note 5), but also to several co-benefits such as biodiversity conservation and job creation for local communities. 
Reforestation in Ghana (left) and afforestation project in China (right). Image by MOL.
MOL Group 5 Sustainability Issues MOL Group will contribute to realize a sustainable society by promoting responses to the sustainability issues, which are identified as social issues that must be addressed with priority through the business. We anticipate this initiative to contribute especially to the realization of "Environment -Conservation for Marine and global environment-" and "Human & Community -Contributing to the growth and development of people and communities-". (Note 1) Voluntary carbon credits Carbon credits, which are one of methods for putting a price on carbon, exist under two schemes; one is mandatory schemes that are created and regulated by the United Nations or national/regional governments, and the other is voluntary schemes that are led and operated by private sectors. Participants in the latter purchase carbon credits on a voluntary basis with no intended use for compliance purposes, so those credits are called "voluntary carbon credits." (Note 2) Climate Neutral Commodity Based in Geneva, Switzerland, it offers services to certify that a series of processes such as calculation of CO2 emissions and retirement of carbon credits conform to international standards such as GHG Protocol and ISO14064, to guarantee transparency in utilization of carbon credits by corporations. Website URL: https://www.climateneutralcommodity.com/ (Note 3) Applied carbon credits 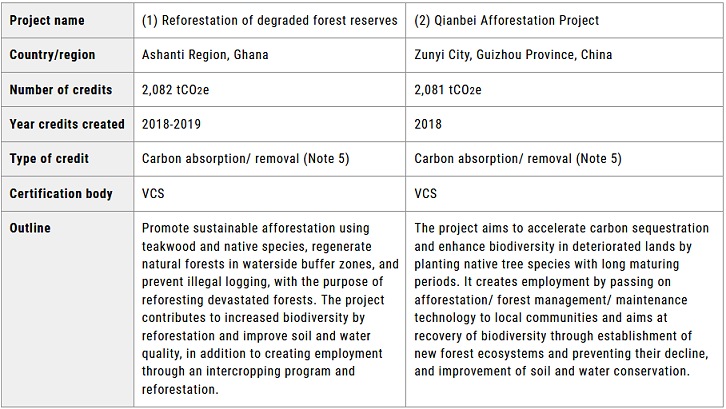
(Note 4) Verra Based in Washington D.C., it is an international carbon credit standard management body that manages and certifies the "Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), which is the most widely used in the world. (Note 5) Types of carbon credits Carbon credits are categorized into two types in comparison to the assumed baseline of emissions in case of BAU (business as usual); the first is derived from emission reduction and avoidance, in which GHG emissions are decreased as the project is implemented; the second is derived from absorption and removal of carbons, in which the volume of GHG absorbed and removed is increased from the baseline. Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. press release 
|
